Waves transport energy and momemtum through space without transporting matter. In this sectionof the learning unit we will discuss the main features of a waves and the methods of transportation.
The figure shows a wave or oscillation. The height of the wave at the maximum displacement (A) is called the Amplitutude
The time taken for a wave to complete one oscillation and return to the original position is called the Period (T). Measured in seconds.
The frequency is the reciprocal of the period f, which is the number of oscillations per second. Measured in Hertz (S -1).
![]()
Wave Types
Wave propagate in two ways Transverse and Longitudinal.
Transverse Wave
 The wave disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. As seen in the figure on the right.
The wave disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. As seen in the figure on the right.
Longitudinal Waves
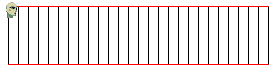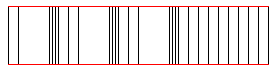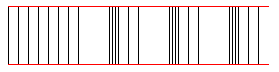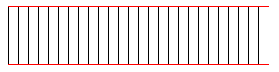 The wave distubance is parallel to the direction of propagation as seen in the figures on the left. Sound is an example of a longitudinal wave.
The wave distubance is parallel to the direction of propagation as seen in the figures on the left. Sound is an example of a longitudinal wave.
Wave Speed
Wave Equation
![]() Newton's laws can be applied to segment of a medium to derive a differential equation known as the wave equation, which relates the spatial derivatives of y(x,t) to a time derivative. The equation can be here, to learn how to derive this equation click here.
Newton's laws can be applied to segment of a medium to derive a differential equation known as the wave equation, which relates the spatial derivatives of y(x,t) to a time derivative. The equation can be here, to learn how to derive this equation click here.